MonitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions is an essential element within the selection, planning, installation, operation and abandonment(wells) Actions taken to ensure permanent isolation of the fluids and pressures of exposed permeable zones within a well from the surface and from lower pressured zones of CO2Carbon dioxide geological storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere sites. MonitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions provides fundamental data about a storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere site's state and performance and thereby helps to meet the common public concern on potential impacts of CO2Carbon dioxide geological storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere on the environment, human health and assets. The main substances of concern are CO2Carbon dioxide and, because of the large volumes, displaced formation waterWater that occurs naturally within the pores of rock formations. MonitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions also includes the observation of impurities within the CO2Carbon dioxide phase, substances mobilised in the subsurface, and geomechanical effects of CO2Carbon dioxide injectionThe process of using pressure to force fluids down wells.
MonitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions programmes implemented at current demo and industrial-scale projects are mostly restricted to the most effective monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions methods (in terms of availability and cost) to comply with the legal and safety requirements. In contrast, a wide variety of monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions tools are developed, adapted, tested and validated at natural release, research and pilot test sites.
Overall, wellManmade hole drilled into the earth to produce liquids or gases, or to allow the injection of fluids-advanced "deep" monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions techniques are available for monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions the performance of the storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere reservoirA subsurface body of rock with sufficient porosity and permeability to store and transmit fluids and tracking the expansion and migrationThe movement of fluids in reservoir rocks of the CO2Carbon dioxide plume. At present, seismic monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions is the dominant geophysical method for the observation of CO2Carbon dioxide in saline aquifers and depleted(hydrocarbon reservoir) one where production is significantly reduced oil reservoirs. Seismic methods allow, in most cases, mapping of the migrationThe movement of fluids in reservoir rocks of the CO2 plumeDispersing volume of CO2-rich phase contained in target formation and, in combination with other measurements, can also provide reasonably accurate volume estimates.
Also, a number of established, reliable methods and tools exist for near-surface monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions at CO2Carbon dioxide storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere sites. The available monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions methods comprise different suites of techniques enabling i) large-scale surveys that contribute to baseline measurements and that can be used to detect eventual leakage(in CO2 storage) The escape of injected fluid from the storage formation to the atmosphere or water column pathways on a regional level, ii) rapid surveying of relatively large areas and derivation of essential results in a short time, iii) detailed small-scale verification(CO2 storage) The proof, to a standard still to be decided, of the CO2 storage using monitoring results; (in the context of CDM) The independent review by a designated operational entity of monitored reductions in anthropogenic emissions and characterisation procedures for selected, confined areas using local knowledge to target possible spots of CO2Carbon dioxide and fluid leakage(in CO2 storage) The escape of injected fluid from the storage formation to the atmosphere or water column. Reliable techniques exist that can distinguish CO2Carbon dioxide from deep origins (geogenic or anthropogenic) from shallow, biogenic CO2Carbon dioxide. In case of leakage(in CO2 storage) The escape of injected fluid from the storage formation to the atmosphere or water column, rates can be quantified by detailed flux measurements. The resolution of the monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions methods and, consequently, the capacity to detect fluid migrationThe movement of fluids in reservoir rocks and irregularities, depends very much on local site conditions and the intensity of monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions. High-resolution measurements obviously increase the detection capacity but require intensive and costly monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions efforts.
The verification(CO2 storage) The proof, to a standard still to be decided, of the CO2 storage using monitoring results; (in the context of CDM) The independent review by a designated operational entity of monitored reductions in anthropogenic emissions activities at five active CO2Carbon dioxide storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere sites showed that monitored site performance deviated from modelled predictions at all sites (Wildenborg et al., 20122013 - Ton Wildenborg, Andy Chadwick, Jean-Pierre Deflandre, Ola Eiken, Allan Mathieson, Richard Metcalfe, Conny Schmidt Hattenberger, Jens WollenweberKey Messages from Active CO2 Storage Sitessee more). Hence, a key element of site-specific monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions plans will be to establish relevant criteria that will allow discrimination between acceptable deviations from the permitted behaviour (which will only necessitate a model update without consequences on the performance prediction of the site) from deviations that represent significant irregularities (and require updates of the riskConcept that denotes the product of the probability of a hazard and the subsequent consequence of the associated event and the monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions plan, and potentially give indications to take remedial actions, change the injectionThe process of using pressure to force fluids down wells plan and eventually require major revisions of the numerical models) (Wildenborg et al., 20122013 - Ton Wildenborg, Andy Chadwick, Jean-Pierre Deflandre, Ola Eiken, Allan Mathieson, Richard Metcalfe, Conny Schmidt Hattenberger, Jens WollenweberKey Messages from Active CO2 Storage Sitessee more). In addition, criteria are needed to evaluate convergence of predicted and observed site performance with time. Such a convergence reflects a sufficient understanding of the storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere system, which is a prerequisite for long-term predictions and the transfer of responsibilityTransfer of all rights and obligations associated with a storage site to a designated authority; will normally be granted when the obligations in the site closure permit has been met with an adequate level of confidence of a storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere site.
The following recommendations for monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions CO2Carbon dioxide storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere site performance are based on extensive experience from groundwater observation, environmental monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions, natural gasGas stored underground; It consists largely of methane, but can also contain other hydrocarbons, water, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide, these other substances are separated before the methane is put into a pipeline or tanker storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere and hydrocarbon production, industrial CO2Carbon dioxide storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere and research pilot projects, the investigation of natural analogues and controlled CO2Carbon dioxide release experiments:
- Comprehensive, integrated, and flexible monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions plans are needed in order to satisfy various monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions needs during normal operation and for contingency monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions. monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions shall form an
| 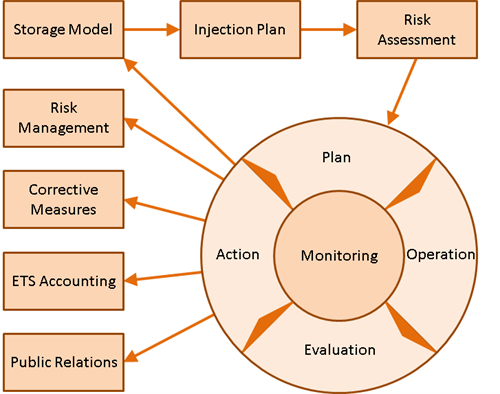
Fig. 5-1: Schematic evolution of site-specific monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions plans in relation to other elements of CO2Carbon dioxide storage(CO2Carbon dioxide) A process for retaining captured CO2Carbon dioxide, so that it does not reach the atmosphereThe layer of gases surrounding the earth; the gases are mainly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (around 21%) management |
integral part of the overall site management and must be continuously improved as wellManmade hole drilled into the earth to produce liquids or gases, or to allow the injection of fluids as any associated activities, as illustrated in Fig. 5-1.
- The development of tools and testing their application at ongoing storage(CO2Carbon dioxide) A process for retaining captured CO2Carbon dioxide, so that it does not reach the atmosphereThe layer of gases surrounding the earth; the gases are mainly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (around 21%) projects under in situ conditions are needed in order to evaluate and provide monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions technologies and concepts considering "new scientific knowledge, and improvements in best available technology", as required by the European CCSCarbon dioxide CaptureThe separation of carbon dioxide from other gases before it is emitted to the atmosphereThe layer of gases surrounding the earth; the gases are mainly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (around 21%) and Storage Directive (2009/31/ECEuropean Commission).
- Cost effectiveness measures, such as campaign optimisation or combination of various methodologies, should be considered. Additionally, it may be beneficial to increase the lifetime of sensors in order to save costs on the maintenance activities.
- The thresholds for acceptable deviations from predictions and the demonstration of convergence must be specified prior to CO2Carbon dioxide injectionThe process of using pressure to force fluids down wells. They should include safety margins, taking into account uncertainties from site characterisation, performance predictions and monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions accuracy. MonitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions plans should be designed in a way that provides appropriate information to verify the specified conditions.
- All stakeholders, including the local population, should be involved in the definition of i) acceptable conditions, ii) significant irregularities and iii) site-specific threshold values. Furthermore, they should participate in the planning of the measures to be taken in the case where such values are exceeded.
- The planning, operation, performance, and updating of monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions activities, such as storage(CO2Carbon dioxide) A process for retaining captured CO2Carbon dioxide, so that it does not reach the atmosphereThe layer of gases surrounding the earth; the gases are mainly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (around 21%) operation in general, should be conducted under independent supervision, e.g. a competent authority, that is not the permitting agency at the same time.
- With respect to detection limits and uncertainties in quantification, the CO2Carbon dioxide injected into a storage(CO2Carbon dioxide) A process for retaining captured CO2Carbon dioxide, so that it does not reach the atmosphereThe layer of gases surrounding the earth; the gases are mainly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (around 21%) formationA body of rock of considerable extent with distinctive characteristics that allow geologists to map, describe, and name it should be regarded as contained within the storage(CO2Carbon dioxide) A process for retaining captured CO2Carbon dioxide, so that it does not reach the atmosphereThe layer of gases surrounding the earth; the gases are mainly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (around 21%) complex, providing that no indication of deviation has been observed by a reasonably extensive, sensitive and appropriate monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions programme.
- Concerning the detection of anomalies and the distinction of storage(CO2Carbon dioxide) A process for retaining captured CO2Carbon dioxide, so that it does not reach the atmosphereThe layer of gases surrounding the earth; the gases are mainly nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (around 21%)-related impacts from natural variations and phenomena, it is essential to integrate the results of near-surface and subsurface monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions efforts in a thorough, systematic and plausible manner. Extensive site-specific knowledge is required because the resolution and sensitivity of many monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions methods (and, hence, the capacity to detect irregularities or fluid migrationThe movement of fluids in reservoir rocks) depend very much on local site conditions and the intensity of monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions.
- The comparison of monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions results with baseline data and model predictions will be crucial for a quantification of effects. Extensive baseline monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions is required for recording natural (e.g. seasonal) variations for relevant parameters that are needed for understanding processes and unravelling the controlling factors for these processes and the resulting variations. Baseline monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions should start wellManmade hole drilled into the earth to produce liquids or gases, or to allow the injectionThe process of using pressure to force fluids down wells of fluids before the first CO2Carbon dioxide injectionThe process of using pressure to force fluids down wells, as part of site characterisation, in order to record secular natural variations and have sufficient time for the interpretation of the recorded data, so that natural processes can be considered in the riskConcept that denotes the product of the probability of a hazard and the subsequent consequence of the associated event and monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions plans.
Some of these issues are currently addressed in ongoing international research projects (e.g. RISCS, ECO2, CO2CARE, SiteChar) and national projects around the world. Once the full range of results is available, it will be possible to further refine monitoringMeasurement and surveillance activities necessary for ensuring safe and reliable operation of a CGS project (storage integrity), and for estimating emission reductions strategies for future CO2Carbon dioxide storage(CO2) A process for retaining captured CO2, so that it does not reach the atmosphere sites.